Introduction: Why Business Analytics Matters Now More Than Ever
In an age where data is considered the new oil, business analytics has become the engine that refines it. From strategy to operations, marketing to HR, companies are using analytics to drive performance. But where did it all begin? Who were the minds that laid the foundation of this transformational discipline?
This post explores:
-
The father(s) of business analytics
-
The historical evolution of the field
-
The importance and benefits
-
The future potential
-
And how you can master and adopt business analytics for career growth
1. The Origin and History of Business Analytics
1.1 Who Is the Father of Business Analytics?
While there isn’t a single universally recognized “father,” several pioneers laid the groundwork. Among the most recognized:
➤ Frederick Winslow Taylor
-
Known for: Scientific Management
-
Contribution: In the early 1900s, Taylor used time-motion studies and performance measurement to increase manufacturing efficiency — a form of early business analytics.
➤ W. Edwards Deming
-
Known for: Statistical Process Control
-
Contribution: Applied data-driven decision-making to improve quality in manufacturing, particularly in post-WWII Japan.
➤ Thomas H. Davenport
-
Known for: Coining the modern term “Business Analytics”
-
Contribution: Authored the influential “Competing on Analytics: The New Science of Winning” (2007), which made analytics mainstream in business strategy.
📚 Source:
1.2 Milestones in Business Analytics History
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1900s | Scientific Management by Taylor |
| 1950s | Statistical Process Control & Deming’s work |
| 1962 | First Business Intelligence system (IBM) |
| 1980s | Rise of Decision Support Systems (DSS) |
| 1990s | ERP systems & SQL data warehouses |
| 2007 | Davenport popularizes analytics |
| 2010s | Emergence of Big Data & AI |
| 2020s | Real-time analytics, predictive models, Gen AI |
2. Importance of Business Analytics
a. Drives Smarter Decision-Making
Analytics shifts decisions from gut-feel to evidence-based.
b. Predicts Trends
Using predictive models, companies can anticipate market behavior and stay ahead of competitors.
c. Enhances Customer Experience
With behavioral analytics and segmentation, companies like Amazon or Netflix personalize user journeys.
d. Optimizes Operations
Logistics, procurement, and HR all benefit from efficiency gains.
📊 Fun Fact:
According to McKinsey, companies using data analytics are 23 times more likely to acquire customers and 19 times more likely to be profitable.
3. Advantages of Business Analytics
| Advantage | Impact |
|---|---|
| Cost Efficiency | Identifies operational inefficiencies |
| Competitive Edge | Offers real-time insights |
| Customer Retention | Drives loyalty with personalization |
| Innovation | Guides product development based on data |
| Scalability | Helps systems grow intelligently |
👉 Read more: McKinsey & Co. Business Analytics Report
4. Scope of Business Analytics in 2025 and Beyond
a. Cross-Industry Applications
-
Retail: Forecasting demand, inventory optimization
-
Finance: Fraud detection, algorithmic trading
-
Healthcare: Predictive diagnostics, patient care modeling
-
Manufacturing: Predictive maintenance, quality control
-
Marketing: Campaign optimization, sentiment analysis
b. Job Roles in Demand
| Role | Avg Salary (USD) |
|---|---|
| Business Analyst | $85,000 – $120,000 |
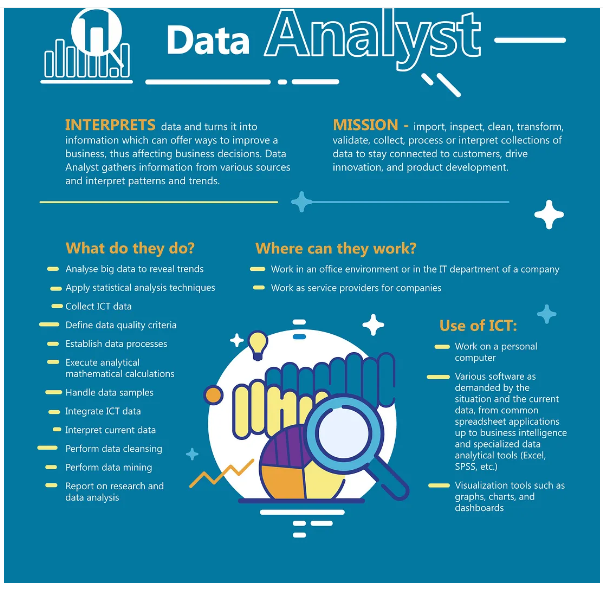
| Data Analyst | $75,000 – $110,000 |
| Data Scientist | $100,000 – $150,000 |
| Analytics Manager | $130,000+ |
| BI Developer | $95,000 – $130,000 |
5. Future of Business Analytics
a. AI & Machine Learning Integration
Automated insights from unstructured data (text, video, audio) will become the norm.
b. Rise of Augmented Analytics
Tools like Tableau, Power BI, and Google Looker are incorporating natural language query engines.
c. Democratization of Data
No-code platforms and self-service BI will empower even non-tech professionals to use data.
d. Gen AI Meets Analytics
GPT-like tools will power faster, contextualized business insights.
🧠 Learn More: Gartner’s Future of Analytics Report
6. How to Adopt Business Analytics: A Roadmap
Step 1: Learn the Fundamentals
Start with:
-
Statistics & Probability
-
Excel, SQL
-
Basic Data Visualization
Free Resources:
Step 2: Get Hands-On with Tools
| Tool | Use |
|---|---|
| Power BI | Dashboard creation |
| Tableau | Data storytelling |
| Excel | Quick analysis |
| Python (Pandas, Matplotlib) | Deeper analytics |
| R | Statistical analysis |
Platforms to Learn:
Step 3: Build Real Projects
-
Analyze sales data for forecasting
-
Customer churn prediction using classification models
-
Create interactive dashboards for marketing KPIs
-
Write blog posts explaining your insights
Upload your projects to:
Step 4: Get Certified
Recommended Certifications:
-
Google Data Analytics (Coursera)
-
Microsoft Power BI Analyst
-
Tableau Desktop Specialist
-
Certified Business Analysis Professional (CBAP)
-
SAS Business Analytics Certification
Step 5: Apply Smartly
-
Target roles in analytics, business intelligence, product strategy
-
Customize your resume with quantifiable metrics
-
Highlight tools + business impact in your case studies
-
Showcase projects on LinkedIn and your own blog
Conclusion
Business Analytics isn’t just a field — it’s a mindset. From its roots in early industrial engineering to today’s AI-powered decision systems, its evolution is a story of technology meeting business.
As we look ahead, analytics will become more embedded, more intuitive, and more powerful. If you adopt this skill now, you’re not just learning data — you’re learning the future language of business.
Want More?
Stay tuned for future blog posts:
-
“Top Business Analytics Projects for Your Resume”
-
“Power BI vs Tableau: Which Should You Learn in 2025?”
-
“The Rise of Augmented Analytics: What You Need to Know”